AI makes 3D images more realistic than ever: RayGauss innovation wins award at WACV 2025



Visual comparison between a 3D Gaussian filter and RayGauss
Novel view synthesis is a technique that allows the generation of images from angles that were not originally captured by a camera. This technology is essential for many applications, ranging from special effects in cinema to 3D mapping for autonomous navigation and virtual reality.
Recent approaches often rely on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), deep learning models that reconstruct a scene by simulating how light interacts with the environment. However, conventional NeRFs have limitations: they require very long computing times and can generate visual artifacts, impairing the quality of the final rendering.
RayGauss offers a new way of creating realistic 3D images using innovative rendering techniques. Rather than relying on ray tracing on a conventional textured mesh, RayGauss takes a different approach: it uses ray tracing with Gaussian-type primitives, which are mathematical ellipsoid shapes, to model both the density of matter and light. In concrete terms, instead of considering a scene as a simple set of surfaces, this method represents matter in the form of diffuse halos, which makes it possible to better capture the way in which light propagates and interacts with objects.
The approach is based on two major advances:
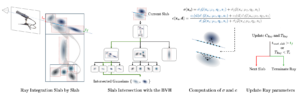
Volumetric rendering algorithm.
One of RayGauss’s great strengths is its balance between quality and efficiency. Unlike other techniques that require several hours of calculation, this method achieves exceptional image quality while maintaining a reasonable training time and real-time performance that can be exploited in concrete applications.
These advances open the way to a variety of uses, particularly in:
The award obtained at WACV 2025 is a major recognition of the work accomplished by the Mines Paris – PSL team. This success illustrates the excellence of French research in artificial intelligence and computer vision, and highlights the role of the Robotics Center (CAOR) and the PR[AI]RIE-PSAI institute in scientific innovation.
The team has made its code publicly available on GitHub, thus promoting the sharing and continuous improvement of this promising technology. RayGauss marks a decisive breakthrough in the field of image synthesis and could well redefine the standards of photorealistic rendering in the years to come.

Comparaisons visuelles : ensemble de données Dex-NeRF